Please complete the form below, and one of our experts will be in touch.
If you would like to send a technical drawing with your enquiry, please email heavysprings@lesjoforsab.com
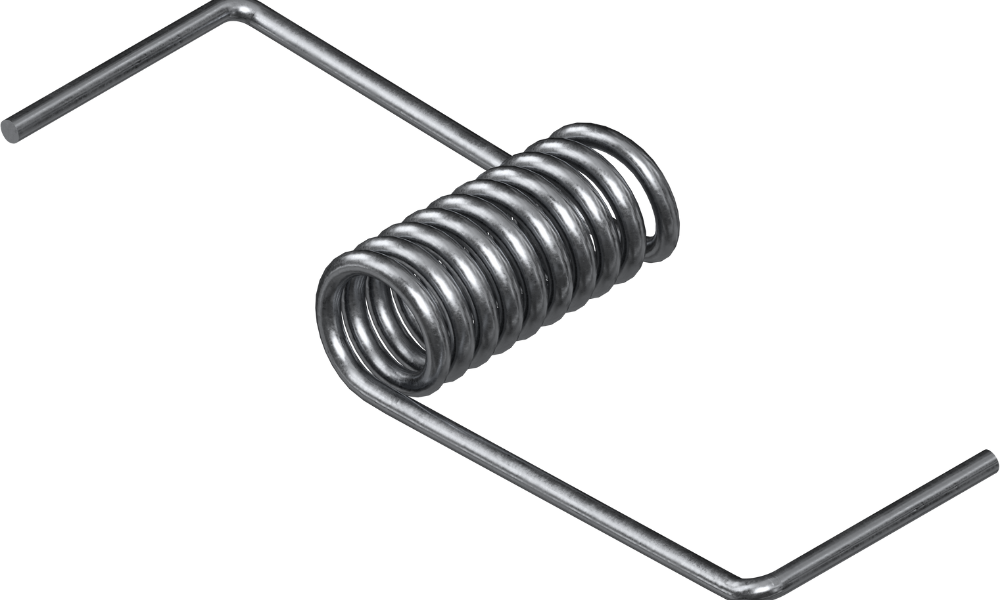

Torsion springs are pivotal components used in various mechanical systems. In this post, we will answer the following questions: What is a torsion spring? How does it work? And what are the different types of torsion springs?
We will also outline the difference between torsion springs and tension springs, enabling you to select the right spring for your application. As expert heavy-duty torsion spring suppliers, we have all the information you need, so let’s get started.
A torsion spring is a mechanical device used to apply rotational force or maintain pressure between surfaces. It exerts torque or rotational force when its two ends are twisted in opposite directions. This type of spring is designed to operate with torque and is commonly used in applications requiring angular movements, such as hinges, hatches, garage doors, lift gates and manhole covers. The performance of a torsion spring depends on its material, diameter, length, and the number of coils.
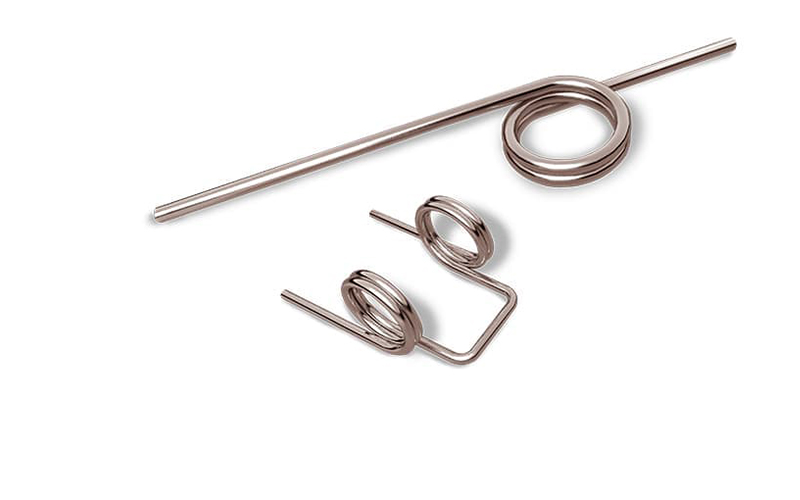

Torsion springs work by storing energy when twisted. When a twisting force is applied, the spring resists the torque and stores energy in the process. Once the force is removed, the spring releases the stored energy, returning to its original position. This action is used to apply rotational force and maintain pressure between surfaces that require angular movement.
In a practical sense, torsion springs are used in numerous industries and everyday applications. Here is a list of items that use torsion springs within each industry.

The torsion spring manufacturing process uses various materials and design variations. Here is an overview of materials, plus the four common types of torsion springs.
Torsion springs are made from similar materials as compression springs. These include types of steel, such as stainless steel for corrosion resistance, high-carbon steel for durability, and alloy steel for enhanced performance in specific applications. Chrome silicone is also used for its ability to withstand high amounts of stress and maximum loads. Some specialised springs might use materials like phosphor bronze or beryllium copper to meet certain requirements, such as electrical conductivity or non-magnetic properties. Nickel coating and galvanised steel treatments may also be used to improve corrosion resistance and resistance to high temperatures.
Axial torsion springs are designed to exert force in a circular motion while the coils remain on a parallel axis to the central rod. This configuration allows for efficient torque transmission along the axis, making them ideal for applications requiring rotational movements with minimal lateral space.
Double torsion springs consist of two coiled parts connected at the centre and wound in opposite directions. This design doubles the effective torque capacity for a given space, offering balanced forces perfect for mechanisms requiring counterbalancing or precise control over large rotational forces.
Tangential torsion springs apply force tangentially, meaning the force is directed along the tangent of the circle formed by the spring. This configuration results in efficient and smooth operation and a direct force application.
Radial torsion springs are characterised by their ability to exert force radially outward from the centre of the spring. This unique design is suitable for applications that require a spreading action or need to counteract inward compression forces, offering a solution where traditional torsion springs may not be applicable.
Torque is usually introduced by a leg form. These forms include tangential legs, axial legs, radial external legs, and radial over-centre legs. Below, you will find an image and a short description of each of these leg forms.
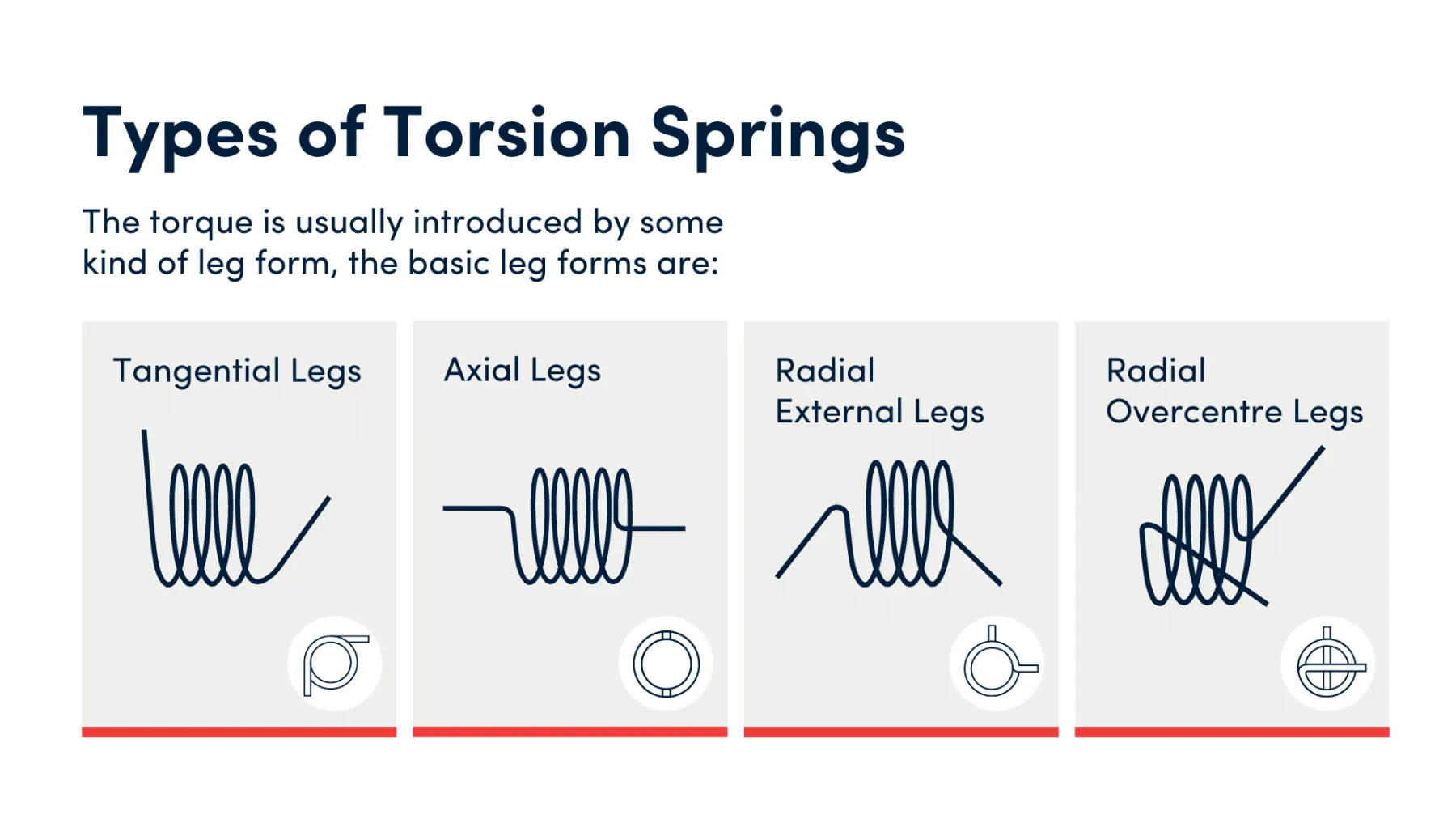
Torsion springs with tangential legs extend at a tangent to the spring's outer diameter, providing a more gradual and controlled application of torque.
Axial legs project along the axis of the spring, ensuring direct and linear force application, ideal for compact spaces.
Radial external legs extend outward from the spring's body, offering robust attachment points for larger mechanisms.
Radial over-centre legs are designed to pass over the spring's centre in operation, enabling a stable and balanced force distribution for precision applications.
The main differences between torsion springs and tension springs include how they store energy and their purpose. A torsion spring stores and releases angular energy, whereas a tension spring stores energy when extended.
Below is a chart that outlines the key differences.
| Torsion Springs | Tension Springs |
|---|---|
| Resists twisting forces | Resists pulling forces |
| Stores energy when twisted | Stores energy when extended |
| Designed to apply rotational force | Designed to pull components together |
| Feature different leg types | Feature different hook types |
Choosing the right spring for your application involves asking the following questions:
Torsion springs offer several advantages, including high efficiency in space utilisation, durability, and versatility in design for custom applications. They provide precise control over torque, which is essential in many mechanical systems, and can be tailored to meet specific needs.
Torsion springs are able to endure many cycles of twisting and provide longevity and consistent performance. This makes them an efficient and durable choice for applications requiring rotational forces.
Torsion springs can be customised for specific needs, with adjustments in size, materials, wire diameter, leg type, and leg angles to meet precise requirements. This flexibility allows for tailored solutions in diverse applications, from small electronics to large industrial machinery.

In modern engineering, torsion springs provide reliable and efficient solutions in applications that require rotational forces. Their ability to store and release energy through rotational movement makes them useful in many devices and systems.
The four common types of torsion springs are axial torsion springs, double torsion springs, tangential torsion springs, and radial torsion springs, which can feature various leg forms. The materials used in torsion springs are similar to those used in other types of springs, with chrome silicone being favoured for its ability to withstand high amounts of stress and maximum loads.
As stockists of the largest global supply of chrome silicon wire, and our ability to manufacture large wire sizes, we are confident that we can design and manufacture tension springs that exert an exceptionally large amount of torque and exceed your expectations.
If you would like to find out more about custom torsion springs, contact our expert team.
Do you need guidance to select the best material for your custom spring?
At Lesjöfors, we work with a large range of materials and hold the largest global stocks of chrome silicon and chrome vanadium anywhere in the world. We can also optimise your spring performance with top-quality materials such as steel, copper and titanium alloys and super alloys, such as Inconel, Hastelloy and Nimonic.
Get in touch with our expert team to receive expert guidance and find out how to order a custom spring.
We are world-leading heavy duty spring manufacturers, delivering the greatest expertise in compression, torsion and tension spring manufacturing.
Delivering impact to every industry, we guarantee spring solutions that will optimise your performance and success.

